Prologue: The Illusion of Prosperity
In the early 2000s, the United States and much of the Western world were riding high on a wave of economic prosperity. The stock market was booming, home prices were soaring, and credit was available to almost anyone who wanted it. The American Dream had never seemed more attainable. But beneath the surface, cracks were forming in the foundations of this seemingly unstoppable growth.
Act 1: The Bubble Inflates (2000-2006)
The origins of the Great Recession can be traced back to a combination of financial deregulation, a booming housing market, and risky lending practices.
- The Role of Subprime Mortgages:
- Banks and financial institutions, encouraged by deregulation, began issuing high-risk loans to borrowers with poor credit histories.
- The subprime mortgage market grew from 8% of total mortgage originations in 2001 to over 20% by 2006.
- Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) turned these risky loans into attractive investments.
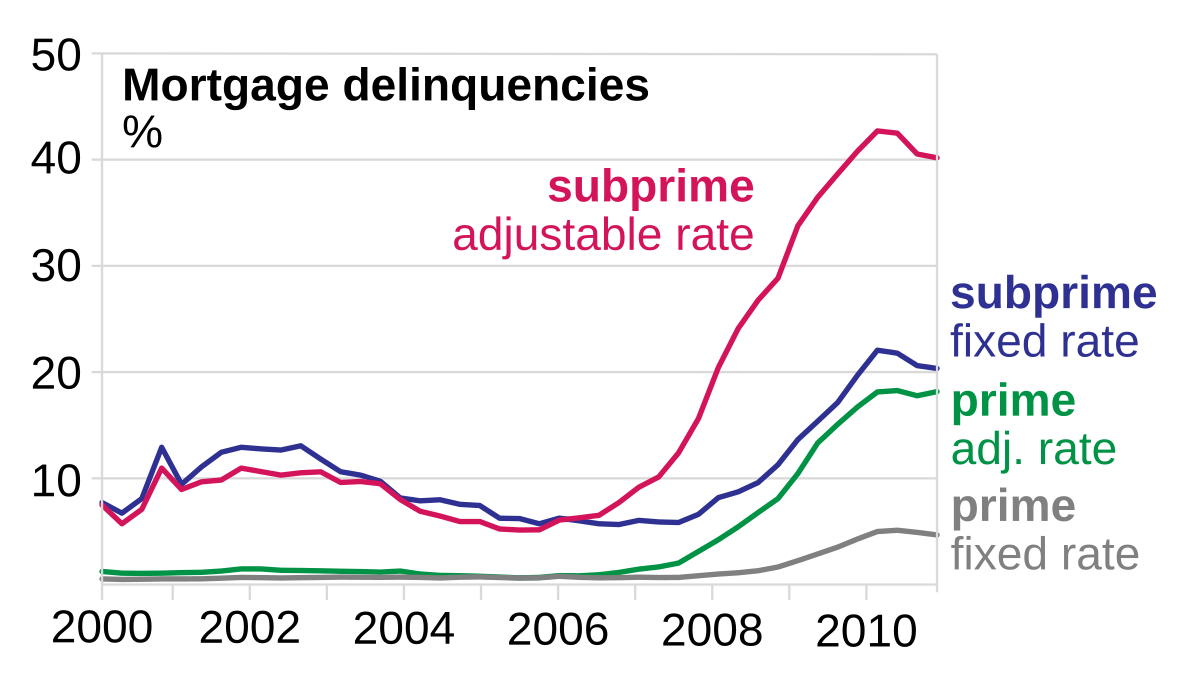
- The Role of the Federal Reserve:
- In response to the dot-com bubble burst in 2000, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates from 6.5% in 2000 to 1% by 2003.
- Cheap credit fueled an artificial boom in housing, encouraging speculative investments.
- Wall Street’s Greed and Financial Engineering:
- Major banks and financial institutions, including Lehman Brothers, Bear Stearns, and AIG, aggressively pushed for the sale of MBS and CDOs.
- Credit rating agencies, such as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s, assigned AAA ratings to these risky securities, falsely signaling their safety to investors.

 Source: Internet
Source: Internet Source: Internet
Source: Internet Source: Internet
Source: Internet