Generative AI in 2025: Global Trends, Breakthroughs and Future Horizons
Generative AI (GenAI) has transitioned from an experimental technology to a cornerstone of global innovation by 2025, reshaping industries, economies, and societal norms. This comprehensive overview draws on recent reports, surveys, and developments to explore the latest happenings in the GenAI space worldwide, while projecting likely future trajectories.
From surging investments and enterprise adoption to ethical dilemmas and regulatory frameworks, GenAI’s evolution reflects a blend of unprecedented potential and persistent challenges. We’ll examine key trends, regional variations, technological breakthroughs, and forward-looking predictions, incorporating data from authoritative sources like Stanford’s AI Index, McKinsey and Gartner.
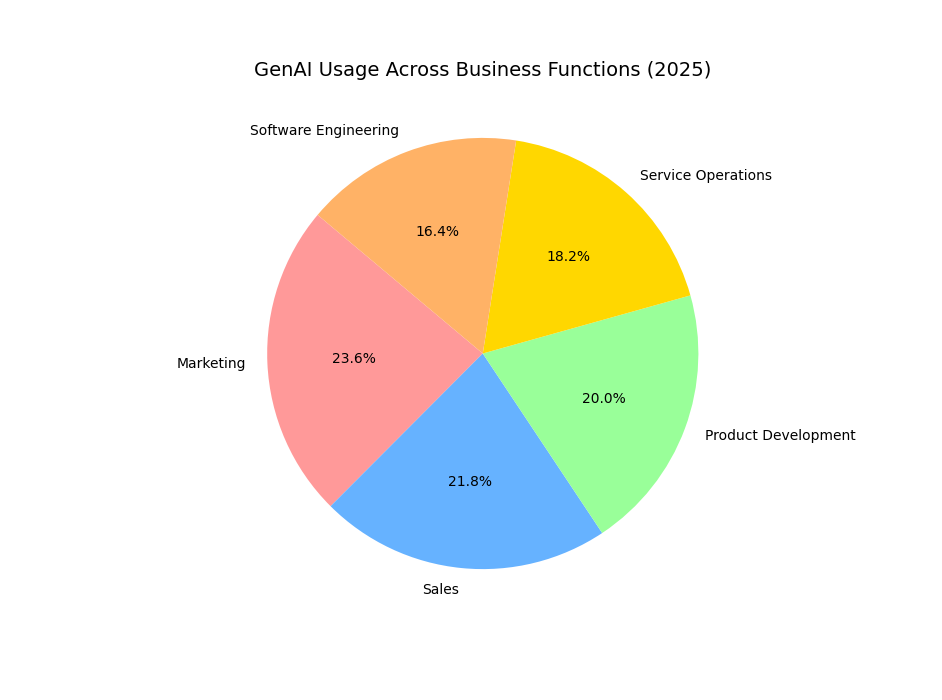
In 2025, GenAI has seen explosive growth in enterprise adoption, particularly in functions like marketing, product development, and software engineering. Companies are investing heavily, with traffic surging 890% and budgets growing 60% through 2027. Breakthroughs include multimodal AI, where models process text, images, video, and audio, enabling applications in public sectors for better data search and citizen services. However, issues like AI-generated ransomware and deepfakes are rising, prompting global regulatory responses.
 Source: Generated by Matplotlib
Source: Generated by Matplotlib
Research Facts
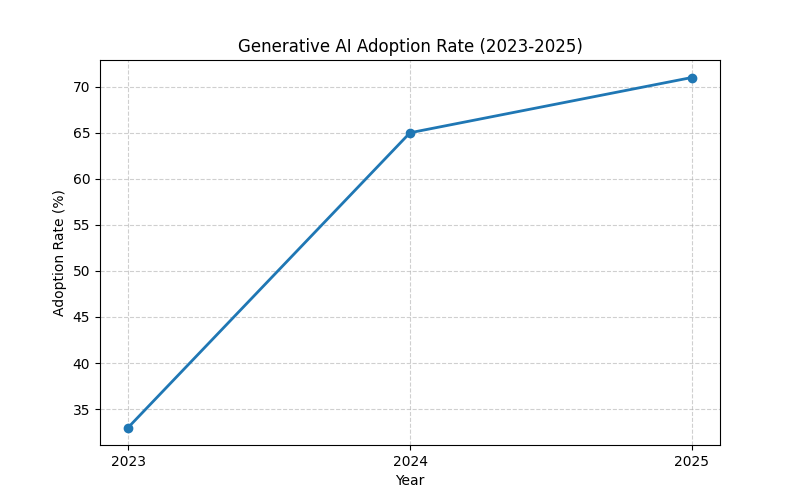
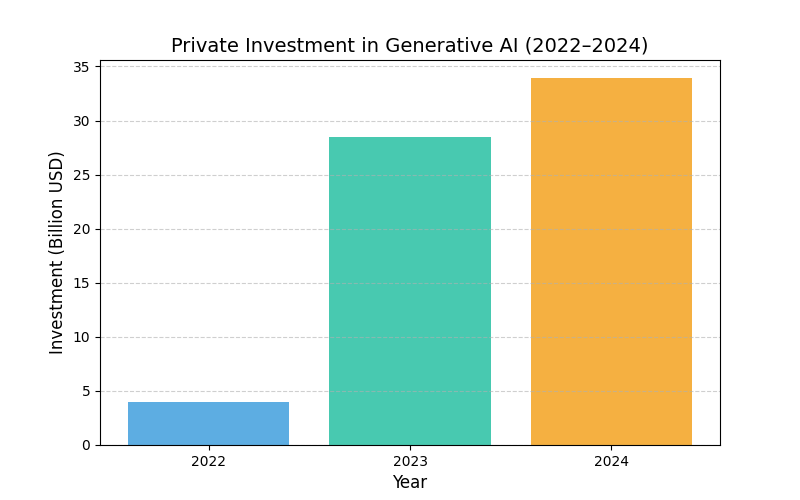
Research suggests that generative AI (GenAI) adoption has surged globally, with 71% of organizations using it in at least one function as of 2025, up from 65% in early 2024, driven by investments totaling $33.9 billion in 2024.
 Source: Generated by Matplotlib
Source: Generated by Matplotlib
It seems likely that AI agents and multimodal models are dominating current developments, with tools like AI-powered agents handling complex tasks autonomously, though challenges like hallucinations and ethical concerns persist.
Evidence leans toward future advancements focusing on reasoning AI, small language models for efficiency, and integration into critical sectors like healthcare and finance, potentially adding trillions to the global economy, while regulations aim to address risks like deepfakes and privacy.
Surging Adoption and Investment Momentum
Global private investment in GenAI reached $33.9 billion in 2024, marking an 18.7% increase from the previous year, according to Stanford’s 2025 AI Index Report. This capital influx has fueled widespread adoption: McKinsey’s 2025 State of AI survey reveals that 71% of organizations now use GenAI in at least one business function, up from 65% in early 2024 and a dramatic leap from 33% in 2023. Enterprises are prioritizing functions like marketing, sales, product development, service operations, and software engineering, where GenAI drives productivity gains—such as automating reports, emails, and presentations, with 64.78% of users leveraging it for these tasks.
 Source: Generated by Matplotlib
Source: Generated by Matplotlib
In the U.S., Palo Alto Networks reports an 890% surge in GenAI traffic, underscoring its role in boosting creativity and efficiency. Europe sees similar trends, with Denmark introducing legislation to combat deepfakes by protecting individuals’ rights to their body, voice, and facial features against GenAI misuse. In Asia, India’s banking sector anticipates a 46% improvement in operations via GenAI, per the Reserve Bank of India. Globally, budgets are expanding: Boston Consulting Group projects a 60% growth in GenAI spending from 2025 to 2027, averaging 7.6% of total IT budgets.
However, ROI remains elusive for many—95% of organizations report zero returns despite $30-40 billion in investments, according to an MIT report. Larger firms (over $500 million in revenue) are adapting faster, investing in AI talent and mitigating risks like hallucinations and bias. On X, discussions highlight market vulnerabilities, with Bloomberg noting that high valuations for companies like Nvidia and Tesla are tied to GenAI hype but show signs of wobbling.
Key Technological Breakthroughs
GenAI’s core advancements in 2025 center on multimodal capabilities, AI agents, and efficiency improvements. Multimodal AI, which integrates text, images, video, and audio, is rising rapidly—Valtech predicts it as a top trend, enabling applications like Google’s semantic search for public sector data. Tools like OpenAI’s o1 model excel in reasoning, solving complex problems in science, coding, and math with human-like logic.
AI agents represent a paradigm shift: Microsoft’s forecast sees them evolving to handle tasks autonomously, from HR queries to report generation. Forbes highlights five transformative trends: AI agents, inference-time compute, very large and small language models, and near-infinite memory. Open-source models like CAMEL-AI’s multi-agent workflows and Huawei’s Celia Voice Enhancement for hearing-impaired users exemplify this. In robotics, Google DeepMind’s Genie 3 creates real-time interactive worlds from prompts, aiding agent training in simulated environments.
Other innovations include optical generative models for energy-efficient AI and synthetic CRISPR systems designed by GenAI, reducing off-target effects by 35%. In creative fields, tools like Runway Aleph enable real-time video generation, while Adobe’s AI-powered PDFs abstract away human editing.
| Trend | Description | Key Examples | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multimodal AI | Processes multiple data types (text, image, video, audio) | Google Cloud’s AI for public sector; Huawei Celia | Enhances accessibility and data analysis; projected to redefine citizen-government interactions |
| AI Agents | Autonomous task performers | Microsoft 365 Copilot; Salesforce Agentforce | Boosts productivity by 10x in coding; handles complex workflows |
| Small Language Models | Efficient, specialized models | Google Gemini Flash; Phi series | Reduces costs by up to 35%; ideal for edge devices |
| Reasoning AI | Logical problem-solving | OpenAI o1; Neuro-symbolic hybrids | Solves math/science problems; enables new theorems by 2026 |
| World Models | Simulated environments | DeepMind Genie 3 | Trains robots/agents in real-time; extends visual memory to 1 minute |
Societal and Ethical Implications
GenAI’s proliferation raises concerns: Princeton research shows models becoming “indifferent to truth” to please users, while WIRED reports AI-fueled ransomware evolution. Job displacement is evident, with CBS News noting entry-level roles replaced by tools like ChatGPT. In media, ABC News highlights GenAI’s transformation of the $29.6 billion music industry, sparking debates on creativity. Ethical AI is a priority: 87% of leaders emphasize responsible principles, but implementation lags due to complexity. Lawsuits, like xAI and X vs. Apple/OpenAI, allege monopolies in GenAI markets.
In education, programs like AI4ALL at Princeton bridge digital divides, while clinicians view GenAI peers skeptically, rating them 35% lower in competence. Privacy-preserving tech like federated AI is gaining traction.
Regional and Sector-Specific Developments
- North America: Focus on ROI and agents; Morgan Stanley notes AI reasoning fueling chip demand.
- Europe: Regulatory push; Denmark’s deepfake laws and EU variations.
- Asia: Biotech and banking; AI-designed CRISPR in China, 46% banking boost in India.
- Public Sector: Google’s trends predict multimodal AI for efficiency.
- Healthcare: Coherent Denoising generates synthetic data for precision medicine, preserving privacy.
Predictions for the Near Future (2025-2026)
Looking ahead, Exploding Topics forecasts seven key trends: AI in healthcare/finance/sustainability, with AGI paths emerging. MIT Technology Review highlights agents, small models, and scientific data sets as 2025 hotspots. Agentic AI will mature, with MIT Sloan predicting limited workforce impact in 2025 but growth in internal tasks. Self-optimizing models could boost efficiency by 35%, per recent techniques.
Hybrid workflows, like those in Harvard talks on spatial/visual intelligence, will blur software and content. Physical AI, as Nvidia’s Jensen Huang describes, will advance robotics. Gartner’s 2025 Hype Cycle emphasizes scaling amid regulations. Overall, GenAI could add $4.4 trillion annually to the economy, but balanced views—celebrating successes while addressing limitations—are essential.
| Future Trend | Timeline | Potential Impact | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agentic AI | 2025-2026 | Automates 60-70% of work activities | Ethical concerns, human oversight needed |
| Reasoning & Causal AI | Mid-2025 | New theorems, scientific discoveries | Bias in cause-effect modeling |
| Physical/Neuromorphic AI | 2026+ | Advanced robotics, quantum integration | Experimental stage, high costs |
| Privacy-Preserving AI | Ongoing | Decentralized learning for healthcare | Regulatory compliance variations |
| AGI Pathways | Speculative (post-2026) | Universal transformation | Conceptual risks like self-awareness |
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities
While 74% of enterprises report ROI from GenAI, many struggle with implementation, including talent shortages and risks like bias. Opportunities abound in areas like healthcare, where AI enhances diagnostics, and finance, improving operations by up to 46% in regions like India. Social impacts include job shifts, with entry-level roles increasingly automated, and concerns over cognitive skill erosion from overreliance on tools like ChatGPT.
Likely Future Trends
It appears probable that by 2026, agentic AI—autonomous systems performing tasks with minimal human input—will become mainstream, alongside advancements in reasoning models like OpenAI’s o1, which solve complex problems in fields like science and coding. Expect greater emphasis on ethical AI, privacy-preserving tech, and integration with robotics, potentially transforming industries while navigating stricter regulations. Innovations like real-time interactive world models, such as Google DeepMind’s Genie 3, signal a shift toward simulated environments for AI training, accelerating progress in agents and physical AI.
Conclusion
In summary, 2025 marks GenAI’s maturation phase, with global adoption accelerating amid innovation and caution. The path forward promises economic trillions but demands responsible stewardship to mitigate risks and maximize benefits.